Eventual vs Strong Consistency
When working with distributed databases, it is important to understand the different concurrent models. Especially when updating data, do we expect all responses to reflect the updated state but incur a performance penalty? Or is performance more important and stale data is acceptable?
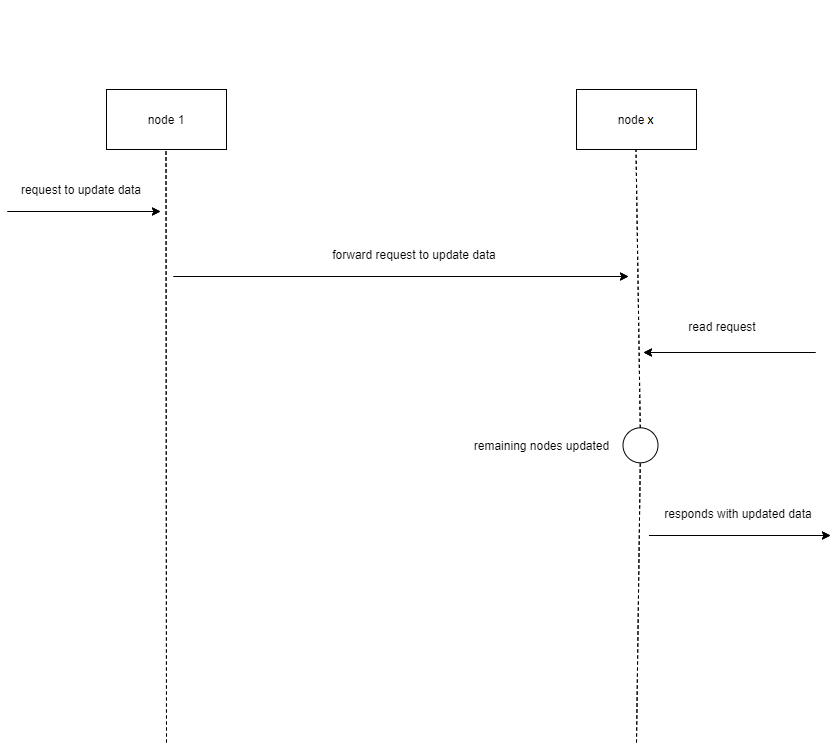
Strong Consistency
Strong Consistency is the concurrency model focused on maintaining accuracy in a distributed database. Simply, when a request to update data is sent to one node, the node will forward the request to all remaining nodes and halts processing. Once all nodes have completed their updates, they can resume processing requests. This ensures the data retrieved will always be up to date but there is a performance implication.
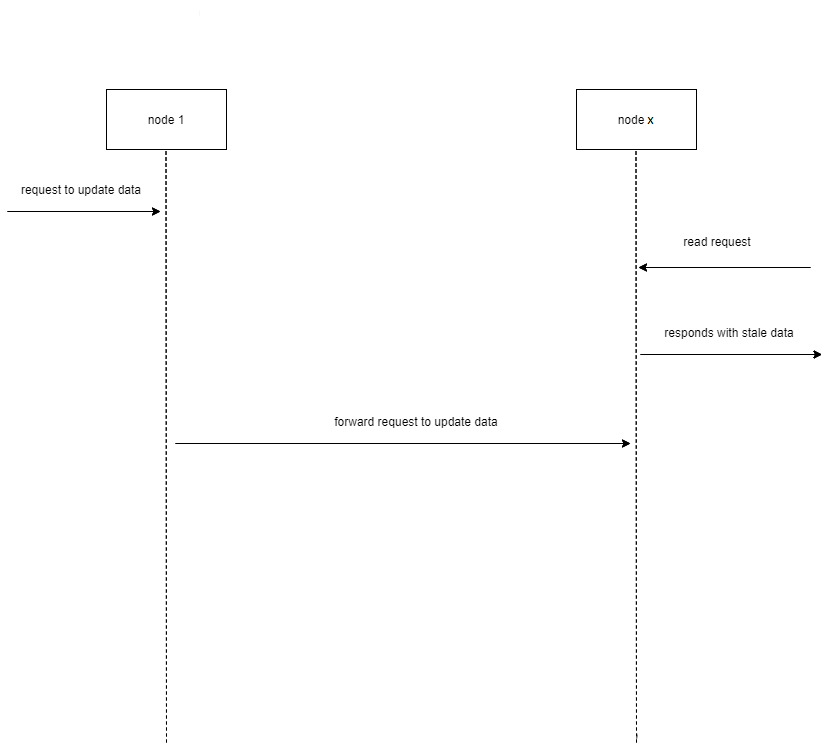
Eventual Consistency
Eventual Consistency model on the other hand, focuses on performance. Eventual consistency differs from strong consistency in that the nodes will continue to process requests (albeit stale data) even when there is a request to update data. Therefore, the distributed database remains performant but sacrifices on accuracy of the data.